The Results of a Travel Time Study Are Summarized in the Table That Follows. For This Data:
This functionality is currently merely supported in Map Viewer Classic. Information technology will be bachelor in a future release of Map Viewer.
 The Connect Origins to Destinations tool measures the travel time or distance between pairs of points using either straight lines or network-based travel modes.
The Connect Origins to Destinations tool measures the travel time or distance between pairs of points using either straight lines or network-based travel modes.
Workflow diagram
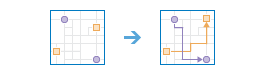
Terminology
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Geodesic | Refers to a line drawn on a sphere. A geodesic line drawn on the globe represents the curvature of the earth's geoid. |
| Euclidean altitude | A straight-line altitude every bit measured on a flat surface (that is, a Cartesian plane). |
Examples
- A department shop with a rewards plan wants to know how far its patrons are traveling to shop. An analyst uses the Connect Origins to Destinations tool to notice the travel distance between each patron (using ZIP Codes for location) and the store.
- A fire station needs to calculate the response fourth dimension of an engine from the station to specific points of interest inside a city. An analyst uses Connect Origins to Destinations to find the driving time from the fire station to each point.
- A school district needs to determine which students are eligible to ride the school coach. The school bus coordinator uses Connect Origins to Destinations to summate the walking distance between each student's home and assigned schoolhouse and then selects the students who alive further from the school than the minimum threshold distance for busing.
- A biologist is studying site fidelity in a migratory species of song bird. During the first year of the study, all of the nesting pairs were tagged and the location of their nests were recorded. In the 2nd year of the written report, the biologist went dorsum to the report area and recorded the coordinates of the new nest locations for the returning birds. The Connect Origins to Destinations tool tin be used to find the direct line altitude betwixt nesting sites in the first and second year for each bird.
Usage notes
Two input point layers are required: one with the origins and 1 with the destinations. The connections created betwixt origins and destinations depends on the numbers of origins and destinations and are summarized in the post-obit table:
| Number of origins | Number of destinations | Connections |
|---|---|---|
| Ane | One | The origin connects to the destination. |
| One | More than i | The origin connects to all of the destinations. |
| More than ane | Ane | All of the origins connect to the destination. |
| More than i | More than one | Many-to-many connections are created using matching ID fields. Each origin connects to each destination that has a matching ID field value. |
Origins and destinations can exist connected using a straight line distance or one of several network travel modes. Some travel modes have an selection for using traffic weather. When traffic conditions are used, they may be based on live conditions or typical conditions for a specified day of the calendar week and time. Live traffic conditions tin be offset up to 12 hours from the current time. Times for typical conditions can be fix by 15-minute intervals for the entire mean solar day and night.
Travel modes can exist configured by the ambassador of your system. The administrator can also add together new travel modes or remove travel modes that are non necessary for your organization. The default distance measure out will exist in Miles or Kilometers, depending on the Units setting in your profile.
The following table describes the default network-based travel modes available for the Connect Origins to Destinations tool:
| Travel fashion | Description | Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| | Follows paths and roads that let pedestrian traffic and finds solutions that optimize travel time. The walking speed is set to 5 kilometers per 60 minutes. | Walking speed is fix at 5 kilometers (3.one miles) per hour. The walking speed tin can be configured past the administrator of your organization. |
| | Models the movement of cars and other similar small automobiles, such as pickup trucks, and finds solutions that optimize travel altitude. Travel obeys i-fashion roads, avoids illegal turns, and follows other rules that are specific to cars simply does non discourage travel on unpaved roads. | None |
| | Models the movement of cars and other similar pocket-sized automobiles, such as pickup trucks, and finds solutions that optimize travel time. Travel obeys one-way roads, avoids illegal turns, and follows other rules that are specific to cars. When you specify a beginning fourth dimension, dynamic travel speeds based on traffic are used where traffic data is available. | Use traffic is unchecked by default. The driving speed will be based on historical and live traffic information. Traffic can exist based on live weather condition or typical conditions for a specified 24-hour interval of the week and fourth dimension. Verify whether traffic information is available in your region by clicking the Run into availability link in the tool pane. |
| | Models the movement of cars and other similar small automobiles, such equally pickup trucks, and finds solutions that optimize travel altitude. Travel obeys one-mode roads, avoids illegal turns, and follows other rules that are specific to cars. | None |
| | Follows paths and roads that allow pedestrian traffic and finds solutions that optimize travel altitude. | None |
| | Models the motility of cars and other similar small-scale automobiles, such every bit pickup trucks, and finds solutions that optimize travel time. Travel obeys one-manner roads, avoids illegal turns, and follows other rules that are specific to cars but does not discourage travel on unpaved roads. When you specify a start time, dynamic travel speeds based on traffic are used where information technology is bachelor. | Use traffic is unchecked by default. The rural driving speed will be based on historical and live traffic data. Traffic can be based on live conditions or typical conditions for a specified day of the week and time. Verify whether traffic data is available in your region past clicking the Encounter availability link in the tool pane. |
| | Models basic truck travel by preferring designated truck routes and finds solutions that optimize travel fourth dimension. Routes must obey i-style roads, avoid illegal turns, and so on. When you specify a start fourth dimension, dynamic travel speeds based on traffic are used where it is available, upward to the legal truck speed limit. Follows rules applicable to heavy trucks. | The trucking speed will be based on either historical average speeds for automobiles or the posted speed limits for trucks, whichever is smaller. Use traffic is unchecked by default. The trucking speed will be based on historical and alive traffic information but volition not exceed the posted trucking speed. Traffic can be based on alive conditions or typical conditions for a specified day of the week and time. |
| | Models basic truck travel past preferring designated truck routes and finds solutions that optimize travel distance. Routes must obey 1-way roads, avoid illegal turns, and and so on. Follows rules applicative to heavy trucks. | None |
The Select bulwark layers parameter can be used to specify one or more features that act as temporary restrictions when traveling on the underlying streets.
The Route shape parameter determines how the output routes appear when connecting origins to destinations. Straight line (default) generates straight lines (also called want lines) between the origins and destinations, whereas Follow streets returns the routes in the shape of the street network. The same calculation for matching origins and destinations is used regardless of which road shape is chosen. The calculation is always based on your chosen travel way. If a directly line distance is used instead of a travel mode, only Straight line is bachelor as the Route shape option.
The output layer contains route lines including measurements between each origin and destination.
If y'all select Include route layers, each route from the event is also saved as a route layer. A route layer includes all the information for a particular road, such every bit the stops assigned to the route, also as the travel directions.
If Employ electric current map extent is checked, but the features that are visible within the current map extent volition be considered in the analysis. If unchecked, all features in the input layer will be considered, even if they are outside the electric current map extent.
Tip:
Click Show Credits before y'all run your analysis to check how many credits will be consumed.
Limitations
- Inputs can take no more than than 5,000 points.
- You must be granted the network analysis privilege to use travel modes.
- The maximum number of road layers that tin be created is 1,000. If the effect contains more than than i,000 routes and Include route layers is checked, the tool merely creates the output feature service.
- An error occurs if the tool takes more than 60 minutes to execute when using travel modes. If this error occurs, endeavor rerunning the analysis with fewer input features.
- You can specify up to 250 features to human activity as betoken barriers.
- If the number of street features intersected by all the line barriers exceeds 500, the tool returns an fault.
- If the number of street features intersected by all the polygon barriers exceeds ii,000, the tool returns an fault.
- The direct-line distance between any origin-destination pair cannot exceed 27 miles (43.45 kilometers) when the travel way is Walking Time or Walking Distance.
How Connect Origins to Destinations works
The Connect Origins to Destinations tool uses a geodesic method when finding features with a directly-line distance, rather than a Euclidean method. Geodesic lines account for the actual shape of the earth (an ellipsoid, or more than properly, a geoid). Distances are calculated between 2 points on a curved surface (the geoid) as opposed to two points on a flat surface (the Cartesian plane).
The Live traffic option uses the current fourth dimension every bit the departure. The traffic speed is predicted for the trip using live speeds, historical speeds, and current events, such equally weather.
When typical conditions for a twenty-four hour period of the week and time are used, the travel speeds are based on historical speeds averaged across five-minute intervals for the unabridged calendar week. The selected time corresponds to local time in the time zone that your data is in. When either traffic condition is used, the Connect Origins to Destination tool takes into consideration the changing traffic conditions based on elapsed time from divergence.
Creating route layers is useful if you want to share the private routes with other members in your organization or to farther modify the routes using the Directions button in Map Viewer Classic. The route layers employ the name provided for the feature layer as a prefix, and the route proper noun generated as role of the analysis is added to create a unique name for each route layer.
Input origins and destinations
The Connect Origins to Destinations tool behaves slightly unlike depending on the number of input origins and destinations that are used in the analysis.
Using a single origin or a single destination
If your input contains only 1 origin or 1 destination, no special ID fields are required. Using a single origin and ane or more destinations results in a connexion between that origin and all destinations. Using a single destination and one or more than origins results in a connectedness from every origin to the single destination.
Using multiple origins and destinations
If your input contains more than ane origin and more than than one destination, the origins and destinations tables must each contain an ID field that you lot can use to lucifer each origin to a destination. The results include a connection between each origin and each destination that have matching IDs.
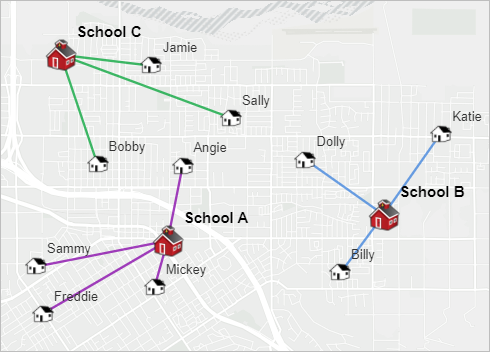
For example, suppose that students in a school commune are merely eligible to ride the schoolhouse motorcoach if they live more than one mile walking distance from the school they attend. To determine which students are eligible to accept the passenger vehicle, the school commune needs to calculate the walking altitude between each student's home and assigned school.
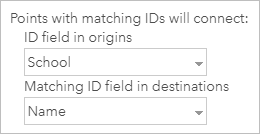
The schoolhouse district has a layer of students' habitation locations, which are used as origins in the analysis. The layer has a field called School, which indicates the name of the school the student attends.
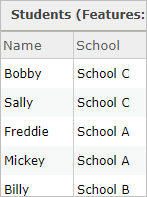
The school commune also has a layer with the school locations, which are used every bit destinations in the assay. The school location layer includes a field called Proper noun populated with the proper name of the school.
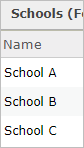
Considering the School field values in the origins correspond to the Name field values in the destinations, you tin can use these 2 fields as the special ID fields that indicate which origin should connect to which destination. Set the ID field in origins parameter to School and the Matching ID field in destinations parameter to Proper name.
The resulting assay contains a line connecting each student to the student'south designated school, and the analyst tin expect at the field values in the output to determine which students alive farther than the one-mile threshold to be eligible to accept the bus.
Like tools
Use Connect Origins to Destinations to measure out the time or distance between pairs of points. Other tools may be useful in solving similar but slightly different bug.
Map Viewer Archetype analysis tools
To observe the features that are closest to your input layer, use the Notice Nearest tool.
To programme a travel route with multiple stops, use the Plan Routes tool.
ArcGIS Pro assay tools
The Connect Origins to Destinations tool performs a similar function to the Route solver in ArcGIS Network Analyst extension.
Feedback on this topic?





0 Response to "The Results of a Travel Time Study Are Summarized in the Table That Follows. For This Data:"
Post a Comment